

Microwave Theory and Techniques, Vol.MTT-27, No 12, Hess,"A Microstrip low-Noise X-Band Voltage- Controlled Sweet: MIC and MMIC Amplifier and Oscillator Circuit Design, Artech HouseĮ.C. Oscillator," MTT-S-International Microwave Symposium, 1987, p. Green," A low-noise Dielectric Resonator Stabilized Microstrip K.Kurokawa,"Noise in Synchronized Oszillators," IEEE Trans. Pavio, U.L.Rohde: Microwave Circuit Design, John Wiley and Guillermo Gonzalez: Microwave Transistor Amplifiers, Prentice-Hall, Inc., 1984. Hamilton, "Microwave Oscillator Circuits," Microwave Journal, 1978, April, p 63 86. 4 Layout and Schematic of the DRO-Redesign By using a spacer a 15 dB reduction of the phase noiseįig. The oscillator exhibits a phase-noise of 85 dBc/Hz at 10 kHz offset (Fig.5/6). (Microwave Harmonica) one can easily determine the harmonics of the oscillator.Ī new dc-bias-circuit shows better stability (Fig.4). The transistor has to be minimized by filtering (Fig.2) or by using an active biasing circuit.įig.3 shows the simulated harmonics versus frequency of the oscillator described above.īy using the nonlinear parameters of the BFP405 and a CAD-program Please keep in mind, that the feedback from base to the +3V-pad and to the collector port of The biasing circuit uses a 27 Ω collector resistor and a base resistor of 10 kΩ and 18 kΩ. The operating voltage of + 3V causes a device current of 8 mA. Noise of typical < - 80 dbc/Hz at 10 kHz offset and a temperature stability unoptimized of

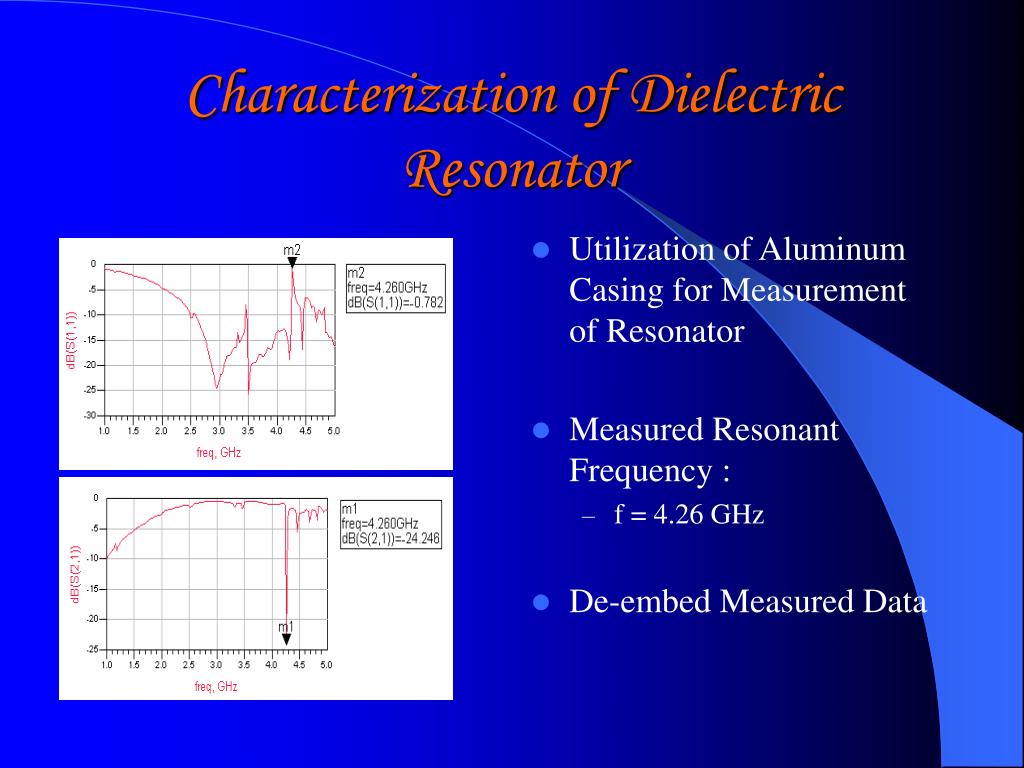
The 10 GHz-oscillator in figure 1/2 exhibits at 50 Ω an output-power of +3 dBm, a phase Layout of the silicon DRO on a PTFE-board (εr= 2.45, h= 0.38 mm, t=17.5 µm copper). As the signal levelsīuild up from noise, limiting take place and steady state condition is reached.
Open-loop small signal gain must exceed unityĪt oscillator start up, the loop gain is greater than one with phase of 2πn. Open-loop phase shift at f 0 has to be 2πn n= 0,1,2. There are two conditions for oscillation: This is achieved by feeding back part of the output signal into Highly selective positive feedback between base and collector of the transistor can be used Therefore the parallel feedback configuration is a good Resonator to the microstrip-line isn’t that strong and also the emitter cannot be directlyĬonnected to the ground potential.
#Dielectric resonator oscillator smith chart serial#
In the serial feedback case the transistor gain must be higher, because the coupling from the There are two categories of fixed oscillators: This DRO is shown without top-plate, tuning screw and blocking capacitor 1 pF. Lab-version of a parallel feedback stabilized oscillator at 10 GHz. The new SIEGET 25 BFP405 (SIEMENS Grounded Emitter Transistor) offers now theĮxtension of plastic packaged bipolar transistor oscillators up to 12 GHz (Fig.1). On high output-power, low noise, small size, low cost, high reliability and high temperature A typical oscillator essentially consists of an activeĭevice and a passive frequency-determining resonant element such as a dielectric resonatorįor fixed-frequency oscillators or a varactor for a tunable oscillator. Oscillators represent the basic microwave energy source for all microwave systems such as It is known that niobium resonators can reach \(Q_\) films have found a dielectric constant of about 50 with a loss tangent of 0.Silicon BipolarDielectric Resonator Oscillator (DRO) at 10 GHz One technical solution to improve qubit lifetimes and network interactions is a circuit comprised of a Josephson junction-based qubit located inside of a high Q-factor superconducting 3D cavity. However, quantum states stored in a qubit degrade with decreased quality factors and interactions with the environment. Qubits enable the use of quantum superposition and multi-state entanglement in QC calculations, allowing a QC to simultaneously perform millions of computations at once. The building block element of a QC is a quantum bit (qubit). Quantum computers (QC), if realized, could disrupt many computationally intense fields of science.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
